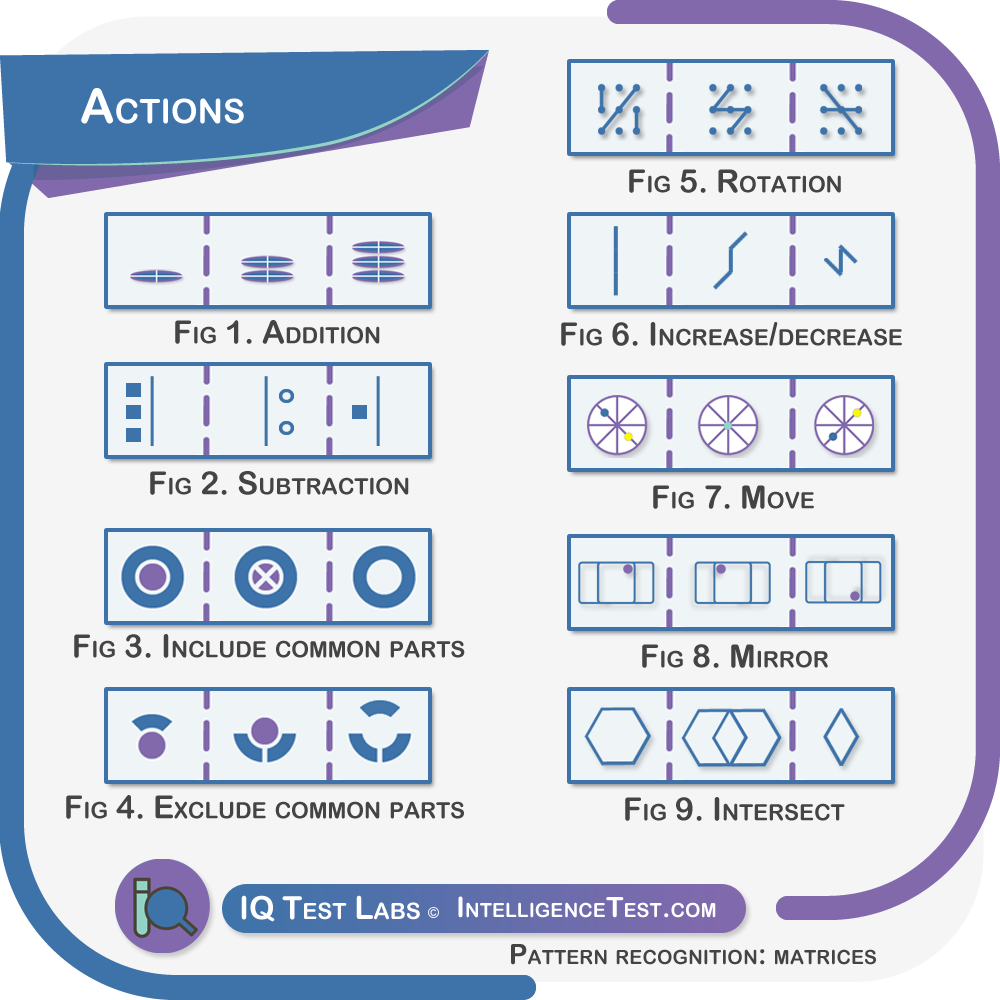
Matrices: actions

- Discover which actions are most likely to be performed on which items.
- Addition/subtraction, and inclusion/exclusion are more common.
- Gaining familiarity with common actions leads to faster solutions and dissolves some of the complexity of more difficult questions.